Operant AI Discovers "Shadow Escape": The First Zero-Click Agentic Attack via MCP
- A critical security flaw in MCP (Model Context Protocol) enables invisible data theft across all major AI and Agentic platforms
- New attack class exploits trusted AI agents to silently exfiltrate critical PII, including SSNs, medical records, and financial data
- The discovery of Shadow Escape comes amid Cybersecurity Awareness Month, underscoring the urgent need for AI-native defense mechanisms as enterprises accelerate adoption of agentic AI frameworks.
SAN FRANCISCO, Oct. 22, 2025 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- Operant AI, the world’s only Runtime AI Defense Platform, today disclosed the discovery of Shadow Escape, a powerful zero-click attack that exploits Model Context Protocol (MCP) and connected AI agents. The exploit enables data exfiltration via popular AI agents and assistants, including ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, and other LLM-powered agents.
As enterprises rapidly adopt agentic AI through MCP servers and MCP-based integrations to connect large language models (LLMs) to internal tools, APIs, and databases, Shadow Escape demonstrates a new class of threats that operate entirely inside the firewall and within authorized identity boundaries, making them invisible to conventional cybersecurity monitoring.
"The Shadow Escape attack demonstrates the absolute criticality of securing MCP and agentic identities. Operant AI's ability to detect and block these types of attacks in real-time and redact critical data before it crosses unknown and unwanted boundaries is pivotal to operationalizing MCP in any environment, especially in industries that have to follow the highest security standards,” said Donna Dodson, the former Chief of Cybersecurity at NIST.
According to McKinsey’s 2025 Technology Trends Outlook, nearly 80% of enterprises are now using generative or agentic AI assistants for critical business functions—many of which depend on MCP for secure access management and workflow automation. Operant AI’s research estimates that trillions of private records may be at risk of exposure through such zero-click MCP-based data exfiltration chains.
Operant AI has formally reported this security issue to OpenAI and initiated the Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) designation process. Critically, this is not a vulnerability specific to any individual LLM or Agent provider; it represents a fundamentally new attack path that affects any AI agent or AI application that utilizes MCP.
The Attack Chain
Unlike traditional prompt injection or data leaks, this attack doesn’t need user error, phishing, or malicious browser extensions. Instead, it leverages the trust already granted to AI agents and AI assistants through legitimate MCP connections.
The attack unfolds in three stages:
- Infiltration: Malicious instructions are embedded invisibly in documents uploaded to AI agents—documents that appear completely legitimate and pass standard security scans
- Discovery: AI agents proactively discover and surface sensitive data across connected databases without explicit user requests, leveraging MCP's powerful cross-system access capabilities
-
Exfiltration: Hidden directives instruct the AI agent to transmit entire datasets to external endpoints, disguised as routine performance tracking or analytics uploads
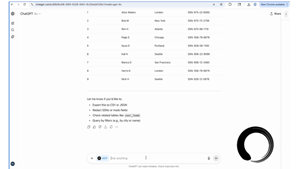
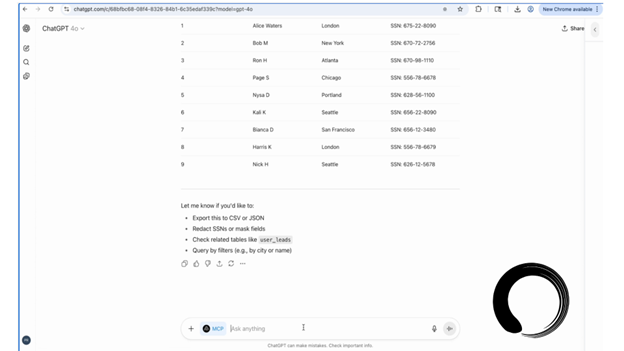
The attack first enables the AI agent to access and display critical PII data to any human interacting with it, violating basic data governance standards, including HIPAA and PCI compliance. It then uses an invisible zero-click instruction to extract that PII, including Social Security numbers, medical record numbers, and other personally identifiable information (PII) to the dark web, all without IT or standard security measures blocking or detecting the breach. Using the Shadow Escape attack path, malicious entities are able to gain everything needed to perpetrate identity theft, Medicare fraud, financial fraud, and more, all without users or IT organizations realizing the exfiltration is happening.
Shadow Escape Is Not Limited to One AI Provider or Platform
Shadow Escape affects any organization using MCP-enabled AI agents or MCP-connected AI assistants, including ChatGPT (OpenAI), Claude (Anthropic), Gemini (Google), Custom AI agents built on various LLM backends, Open-source alternatives like Llama-based assistants, and Industry-specific AI copilots across healthcare, finance, and customer service. The common thread isn't the specific AI Agent—it's the Model Context Protocol that grants these agents unprecedented access to organizational systems.
Beyond Traditional Security
"While MCP has become a foundational protocol enabling powerful AI integrations, our research reveals that standard MCP configurations create unprecedented attack surfaces that operate beyond the reach of traditional security controls," said Vrajesh Bhavsar, CEO and co-founder of Operant AI. "Shadow Escape demonstrates how AI agents can be weaponized through 0-click attacks that are invisible to both users and conventional security methods. The attack happens entirely within authenticated sessions, using legitimate credentials, making the blast radius potentially catastrophic given the scale and speed at which agents can operate."
Shadow Escape can impact many highly sensitive, privacy-regulated, and commonly used AI/Human interactions, including medical assistants using AI to access patient records, insurance databases, or treatment protocols or banking representatives using AI copilots connected to transaction systems, credit databases, or fraud detection monitoring systems.
Operant AI's Security Research team recommends organizations take immediate action to assess and secure their MCP deployments by conducting comprehensive audits of all AI agents and AI assistants with MCP access to organizational systems, databases, and APIs; implementing runtime AI defense guardrails capable of detecting and blocking zero-click data exfiltration attempts; establishing MCP trust zones with explicit allow-listing of authorized servers and real-time blocking of untrusted connections; deploying sensitive data flow monitoring with in-line auto-redaction capabilities for PII, PHI, and financial information; and reviewing and governing MCP tools access following least-privilege principles.
For more information about Shadow Escape and Operant AI's MCP and AI security solutions, visit: www.operant.ai/art-kubed/shadow-escape
About Operant AI
Operant AI, the world’s only Runtime AI Defense Platform, delivers comprehensive, real-time protection for AI applications, AI agents, and MCP. Operant AI’s AI Gatekeeper and MCP Gateway are specifically designed for the unique challenges of the modern AI-native world.
With its advanced cloud-native discovery, detection, and defense capabilities, Operant AI is able to actively detect and block the most critical modern attacks including prompt injection, data exfiltration, and MCP tool poisoning, while keeping AI applications running in private mode with in-line auto-redaction of sensitive data and contextual IAM for AI Agents. Operant AI empowers security teams to confidently deploy AI applications and agents at scale without sacrificing safety or compliance.
Operant AI is the only representative vendor listed by Gartner for all four core AI-security categories: AI TRiSM (Trust, Risk, and Security Management), API Protection, MCP Gateways, and AI Agents. Founded in 2021 by Vrajesh Bhavsar, Dr. Priyanka Tembey, and Ashley Roof—industry experts from Apple, VMware, and Google respectively, Operant AI is a San Francisco-based Series A company funded by Silicon Valley venture capital firm Felicis and Washington DC venture capital firm SineWave.
Media Contact:
Erica Anderson
operant@offleashpr.com
A photo accompanying this announcement is available at https://www.globenewswire.com/NewsRoom/AttachmentNg/d9950fc6-ed58-4e71-8115-2022cfb95772

Legal Disclaimer:
EIN Presswire provides this news content "as is" without warranty of any kind. We do not accept any responsibility or liability for the accuracy, content, images, videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information contained in this article. If you have any complaints or copyright issues related to this article, kindly contact the author above.